Stationary Directional Source Modeling
| Symbol | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| $\mathbf{b}_\mathrm{s}(t)$ | vector function of time | time-varying (rotating) source beam center |
| $\mathbf{b}_\mathrm{r}(t)$ | vector function of time | time-varying (rotating) receiver beam center |
| $\Theta(t)$ | scalar function of time | angle relative to time-varying beam center |
| $\angle(\bm{u},\bm{v})$ | operator | returns the angle between two vectors |
| $\mathrm{G}_\mathrm{s}(\Theta)$ | scalar function of angle | Gain of the source antenna |
| $\mathrm{G}_\mathrm{r}(\Theta)$ | scalar function of angle | Gain of the receiver antenna |
| $\mathrm{D}_\mathrm{s}\big(\bm{\xi};\,{\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s},\mathbf{b}_\mathrm{s}(\cdot)}\big)$ | scalar function of position | directivity of source |
| $\mathrm{D}_\mathrm{r}\big(\bm{\xi};\,{\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{r},\mathbf{b}_\mathrm{r}(\cdot)}\big)$ | scalar function of position | directivity of receiver |
| $\mathsf{h}\big(\bm{\xi},t;\,{\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s},\mathbf{b}_\mathrm{s}(\cdot),\mathrm{G}_\mathrm{s}(\cdot)}\big)$ | scalar function of position and time | LTI impulse response from $\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}$ to $\bm{\xi}$ |
| $\mathsf{g}\big(\bm{\xi},t;\,{\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{r},\mathbf{b}_\mathrm{r}(\cdot),\mathrm{G}_\mathrm{r}(\cdot)}\big)$ | scalar function of position and time | LTI impulse response from $\bm{\xi}$ to $\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{r}$ |
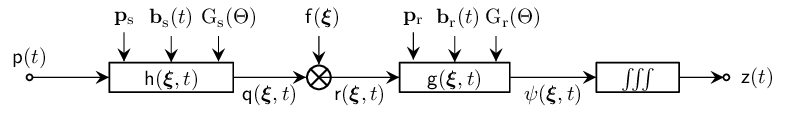
The LTI impulse response from $\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}$ to $\bm{\xi}$ is given by
\[\mathsf{h}\big(\bm{\xi},t;\,{\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s},\mathbf{b}_\mathrm{s}(\cdot),\mathrm{G}_\mathrm{s}(\cdot)}\big) = \mathrm{D}_\mathrm{s}\big(\bm{\xi};\,{\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s},\mathbf{b}_\mathrm{s}(\cdot)}\big) \mathsf{A}\left(\frac{\|\bm{\xi}-\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}\|} {\mathrm{c}}\right) \delta\left(t-\frac{\|\bm{\xi}-\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}\|}{\mathrm{c}}\right),\]
where $\mathrm{D}_\mathrm{s}\big(\bm{\xi};\,{\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s},\mathbf{b}_\mathrm{s}(\cdot)}\big)$ is the directional gain defined by
\[\mathrm{D}_\mathrm{s}\big(\bm{\xi};\,\textcolor{myLightSlateGrey} {\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s},\mathbf{b}_\mathrm{s}(\cdot)}\big)= \mathrm{G}_\mathrm{s} \big(∠[\,\mathbf{b}(\cdot)\,,\,\bm{\xi}-\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}\,]\big).\]
The signal observed at position $\bm{\xi}$ and time $t$ due to the source emitting from position $\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}$ is given as
\[\begin{aligned} \mathsf{q}(\bm{\xi},t) &= \mathsf{p}(t) \overset{t}{*} \mathsf{h}\big(\bm{\xi},t;\,{\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s},\mathbf{b}_\mathrm{s}(\cdot),\mathrm{G}_\mathrm{s}(\cdot)}\big) \\ &=\mathrm{D}_\mathrm{s}\big(\bm{\xi};\,{\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s},\mathbf{b}_\mathrm{s}(\cdot)}\big) \mathsf{A}\left(\frac{\|\bm{\xi}-\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}\|} {\mathrm{c}}\right) \mathsf{p}\left(t-\frac{\|\bm{\xi}-\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}\|}{\mathrm{c}}\right). \end{aligned}\]
The reflection due to source is given by
\[\mathsf{r}(\bm{\xi},t) = \mathsf{f}(\bm{\xi}) \mathsf{q}(\bm{\xi},t).\]
The LTI impulse response from an arbitrary position $\bm{\xi}$ to the receiver at position $\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{r}$ is given by
\[\mathsf{g}\big(\bm{\xi},t;\,{\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{r},\mathbf{b}_\mathrm{r}(\cdot),\mathrm{G}_\mathrm{r}(\cdot)}\big) = \mathrm{D}_\mathrm{r}\big(\bm{\xi};\,{\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{r},\mathbf{b}_\mathrm{r}(\cdot)}\big)\mathsf{A}\left(\frac{\|\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{r}-\bm{\xi}\|}{\mathrm{c}}\right) \delta\left(t-\frac{\|\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{r}-\bm{\xi}\|}{\mathrm{c}}\right).\]
where $\mathrm{D}_\mathrm{r}\big(\bm{\xi};\,{\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{r},\mathbf{b}_\mathrm{r}(\cdot)}\big)$ is the directional gain defined by
\[\mathrm{D}_\mathrm{r}\big(\bm{\xi};\,\textcolor{myLightSlateGrey} {\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{r},\mathbf{b}_\mathrm{r}(\cdot)}\big)= \mathrm{G}_\mathrm{r} \big(∠[\,\mathbf{b}(\cdot)\,,\,\bm{\xi}-\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{r}\,]\big).\]
The signal observed at $\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{r}$ due to the reflection from the position $\bm{\xi}$ is given by
\[\begin{aligned} \mathsf{\psi}(\bm{\xi},t) &= \mathsf{r}(\bm{\xi},t) \overset{t}{*} \mathsf{g}\big(\bm{\xi},t;\,{\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{r},\mathbf{b}_\mathrm{r}(\cdot),\mathrm{G}_\mathrm{r}(\cdot)}\big) \\ &= \mathsf{A}\left(\frac{\|\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{r}-\bm{\xi}\|}{\mathrm{c}}\right) \mathsf{r}\left(\bm{\xi},t-\frac{\|\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{r}-\bm{\xi}\|}{\mathrm{c}}\right). \end{aligned}\]
Scenario A [Pulse train, multiple reflector, transmitter and receiver at same location]
Scenario Assumptions
- single stationary directional source with time-varying (rotating) beam center
- single stationary receiver at same location as the source
- multiple stationary ideal point reflectors at different radial distances
- the source emits a periodic impulse train
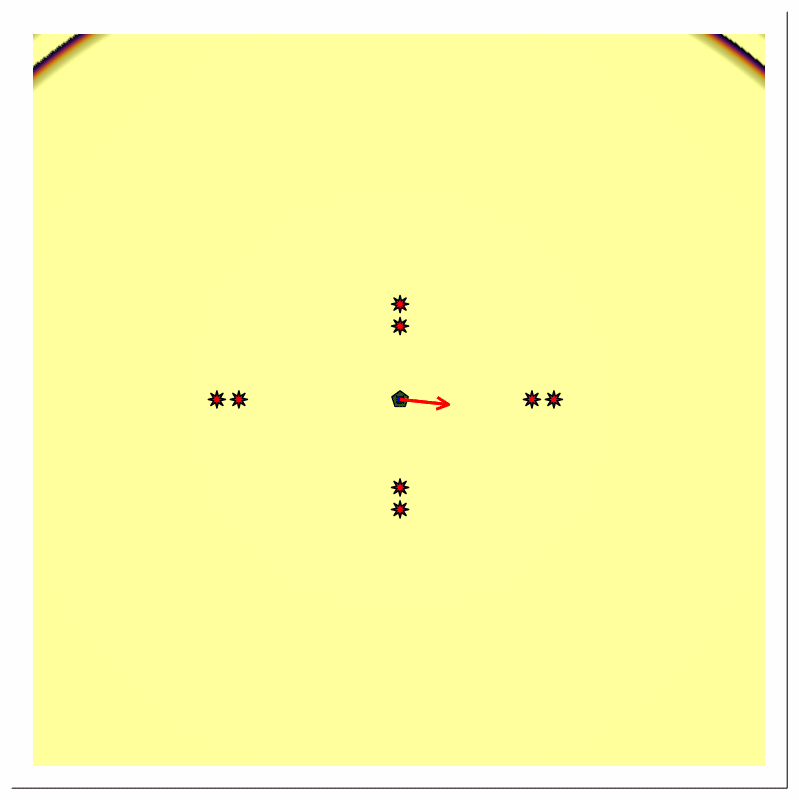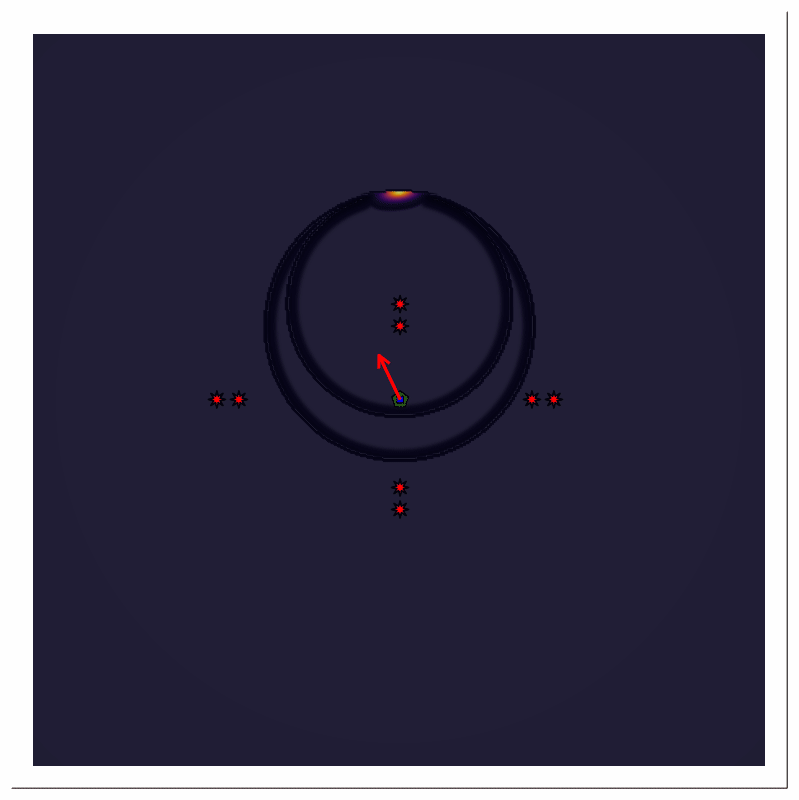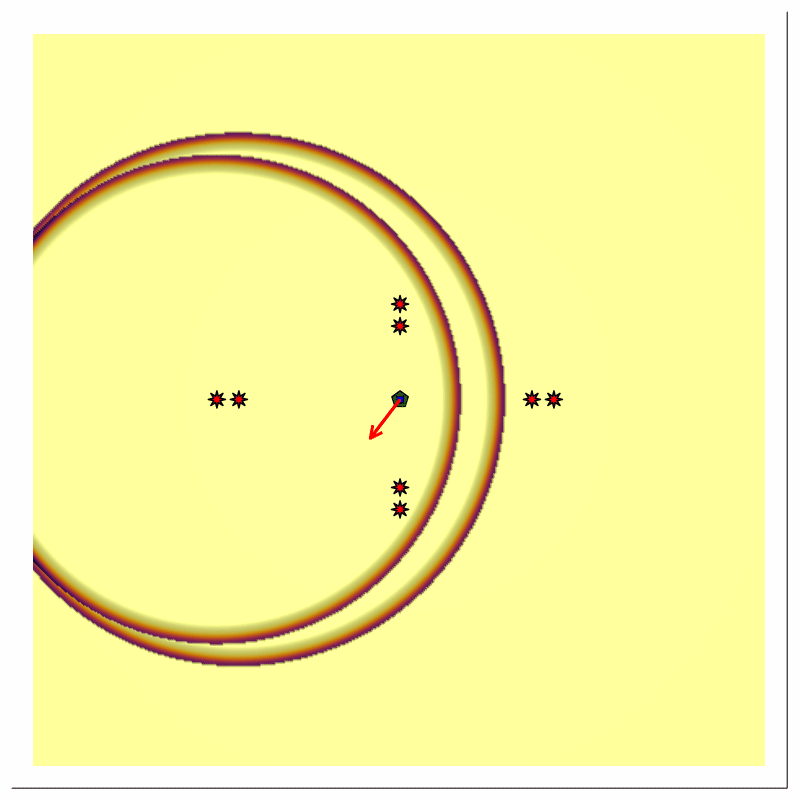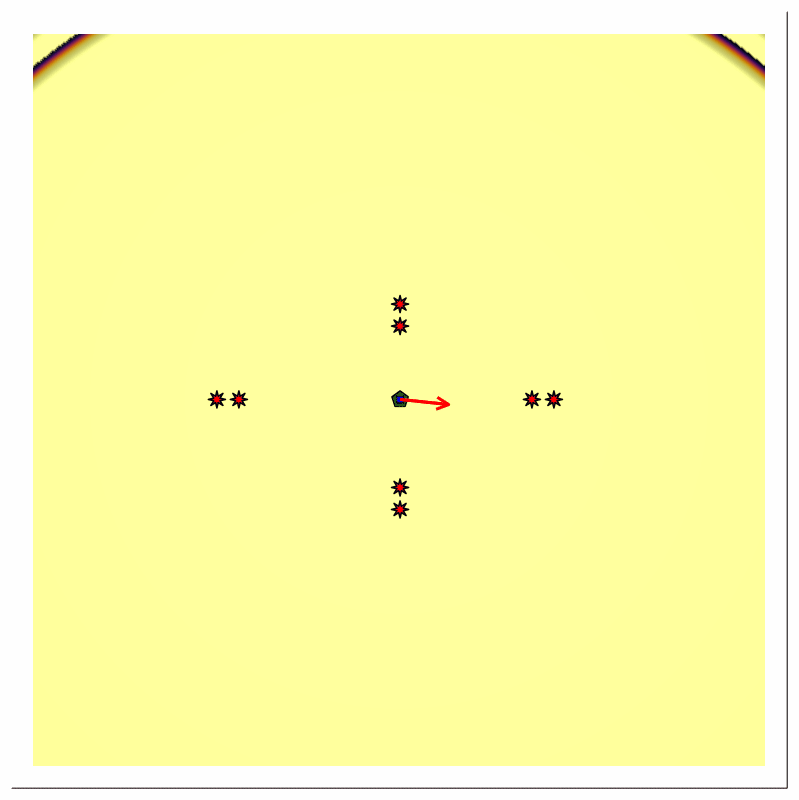
Forward Modeling
For scenario A, we provided the position of the stationary directional source $𝐩ₛ$, with time-varying (rotating) beam center $𝐛(t)$, the stationary receiver's position $𝐩ᵣ$, being at the same location $(𝐩ₛ=𝐩ᵣ)$, the transmitted signal $\mathsf{p}(t)$, and multiple reflector say, N.
Now the expression for the reflector function is given by
\[\mathsf{f}(\bm{\xi}) = \sum\limits_{n=1}^{N}\mathsf{\alpha}_n \delta(\bm{\xi} - \bm{\xi}_n).\]
We compute the reflection due to the directional source as follows
\[\mathsf{r}(\bm{\xi},t) = \sum\limits_{n=1}^{N}\mathsf{\alpha}_n \delta(\bm{\xi} - \bm{\xi}_n) \mathrm{D}_\mathrm{s}\big(\bm{\xi};\,{\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s},\mathbf{b}_\mathrm{s}(\cdot)}\big) \mathsf{A}\left(\frac{\|\bm{\xi}-\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}\|} {\mathrm{c}}\right) \mathsf{p}\left(t-\frac{\|\bm{\xi}-\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}\|}{\mathrm{c}}\right).\]
Finally, the closed form expression of the observed signal, $\mathsf{z}(t)$ is given by
\[\mathsf{z}(t) = \sum\limits_{n=1}^{N} \mathsf{\alpha}_n \mathrm{D}_\mathrm{s}\big(\bm{\xi}_n;\,{\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}, \mathbf{b}_\mathrm{s}(\cdot)}\big)\mathsf{A}^2 \left(\frac{\|\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}-\bm{\xi}_n\|} {\mathrm{c}}\right)\mathsf{p}\left(t -2\frac{\|\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}-\bm{\xi}_n\|}{\mathrm{c}}\right).\]
using LTVsystems
using Plots
𝐩ₛ = [0.0, 0.0]
𝐩ᵣ = [0.0, 0.0]
tₚ = 1.0e-06
T = 15.0e-6
M = 4
p(t) = δn(mod(t-tₚ,T),1.0e-07)
α₁ = -0.7; 𝛏₁ = [0.21c*T,0.0]
α₂ = -0.7; 𝛏₂ = [0.0,0.10c*T]
α₃ = -0.7; 𝛏₃ = [-0.22c*T,0.0]
α₄ = -0.7; 𝛏₄ = [0.0,-0.15c*T]
α₅ = -0.7; 𝛏₅ = [0.18c*T,0.0]
α₆ = -0.7; 𝛏₆ = [0.0,0.13c*T]
α₇ = -0.7; 𝛏₇ = [0.0,-0.12c*T]
α₈ = -0.7; 𝛏₈ = [-0.25c*T,0.0]
f₀ = 1/(M*T)
𝐛(t) = [cos(2π*f₀*(t-tₚ)),sin(2π*f₀*(t-tₚ))]
G(θ) = 𝒩ᵤ(θ, μ=0.0, σ=π/64)
q = STATsourceD(𝐩ₛ,p,𝐛,G)
r = pointReflector([𝛏₁,𝛏₂,𝛏₃,𝛏₄,𝛏₅,𝛏₆,𝛏₇,𝛏₈],[α₁,α₂,α₃,α₄,α₅,α₆,α₇,α₈],[q])
z = LTIreceiverO(r,𝐩ᵣ)
t=0.0:T/500:M*T
p1 = plot(t,p, xlab="time (sec)", ylab="p(t)", legend=:false)
p2 = plot( t, z(t),ylims=(minimum(z(t)),maximum(z(t))), xlab="time (sec)", ylab="z(t)", legend=:false)
plot(p1,p2,layout=(2,1),size=(800,800))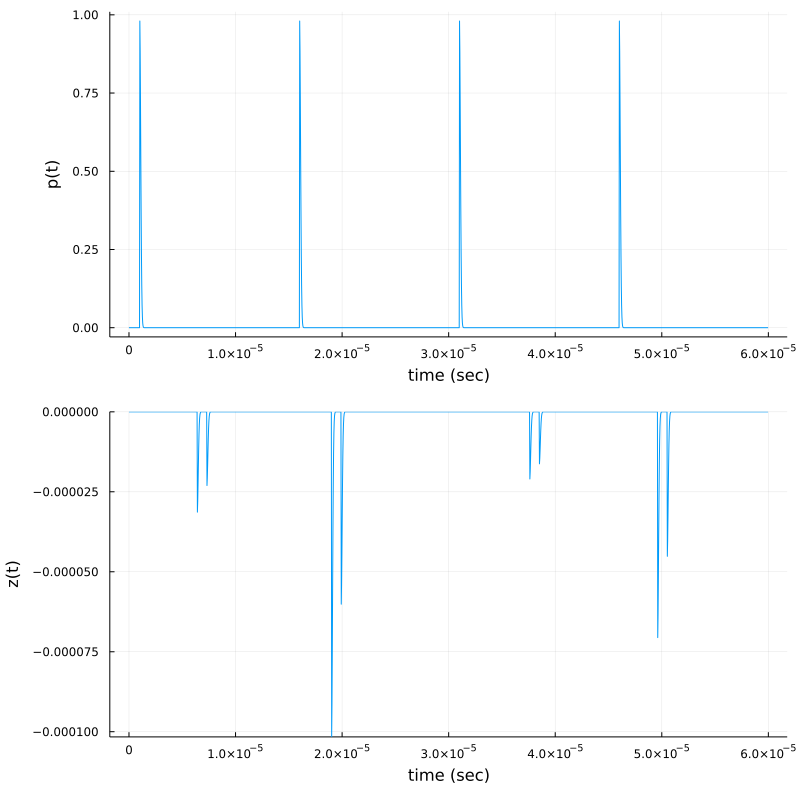
Inverse Modeling
Given the scenario A assumptions, we obtained the received signal, $\mathsf{z}(t)$. Now by considering the transmitted signal as a pulse train given by
\[\mathsf{p}(t)=δ(\mathrm{mod}(t-t_\mathrm{p},\mathrm{T})),\]
we compute the reflector function as follows
\[\hat{\mathsf{f}}(\bm{\xi}) = ∑_{k=1}^{M} \mathsf{f}_k(\bm{\xi}),\]
where $M$ is the number of pulses and $\mathsf{f}_k$ is the reflector function with respect to each periodic pulse given by
\[\mathsf{f}_k(\bm{\xi})=\dfrac{\mathsf{z}\left(t_\mathrm{p}+(k-1)\mathrm{T}+\frac{2\|\bm{\xi}-\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}\|}{\mathrm{c}}\right)\mathrm{D}_{\mathrm{s}k}(\bm{\xi})}{\mathsf{A}^2\big(\frac{\|\bm{\xi}-\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}\|}{\mathrm{c}}\big)},\]
where $\mathrm{D}_{\mathrm{s}k}(\bm{\xi}) = \mathbf{G}\big(∠(𝐛(t_\mathrm{p}+(k-1)\mathrm{T}), \bm{\xi}.-\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s})\big).$
using LTVsystems
using Plots
𝐩ₛ = [0.0, 0.0]
𝐩ᵣ = [0.0, 0.0]
tₚ = 1.0e-06
T = 15.0e-6
M = 4
p(t) = δn(mod(t-tₚ,T),1.0e-07)
α₁ = -0.7; 𝛏₁ = [0.21c*T,0.0]
α₂ = -0.7; 𝛏₂ = [0.0,0.10c*T]
α₃ = -0.7; 𝛏₃ = [-0.22c*T,0.0]
α₄ = -0.7; 𝛏₄ = [0.0,-0.15c*T]
α₅ = -0.7; 𝛏₅ = [0.18c*T,0.0]
α₆ = -0.7; 𝛏₆ = [0.0,0.13c*T]
α₇ = -0.7; 𝛏₇ = [0.0,-0.12c*T]
α₈ = -0.7; 𝛏₈ = [-0.25c*T,0.0]
f₀ = 1/(M*T)
𝐛(t) = [cos(2π*f₀*(t-tₚ)),sin(2π*f₀*(t-tₚ))]
G(θ) = 𝒩ᵤ(θ, μ=0.0, σ=π/64)
q = STATsourceD(𝐩ₛ,p,𝐛,G)
r = pointReflector([𝛏₁,𝛏₂,𝛏₃,𝛏₄,𝛏₅,𝛏₆,𝛏₇,𝛏₈],[α₁,α₂,α₃,α₄,α₅,α₆,α₇,α₈],[q])
z = LTIreceiverO(r,𝐩ᵣ)
Dₛₖ(ξ::Vector{Float64},k::Int64) = G(angleBetween(𝐛(tₚ+(k-1)*T), ξ.-𝐩ₛ))
fₖ(ξ::Vector{Float64},k::Int64) = ifelse(norm(ξ)>c*T/2, NaN, (z(tₚ+(k-1)*T+(2norm(ξ-𝐩ₛ))./c).*Dₛₖ(ξ,k)./(A(norm(ξ-𝐩ₛ)/c))^2))
g(ξ::Vector{Float64}) = sum(fₖ(ξ,k) for k ∈ 1:M)
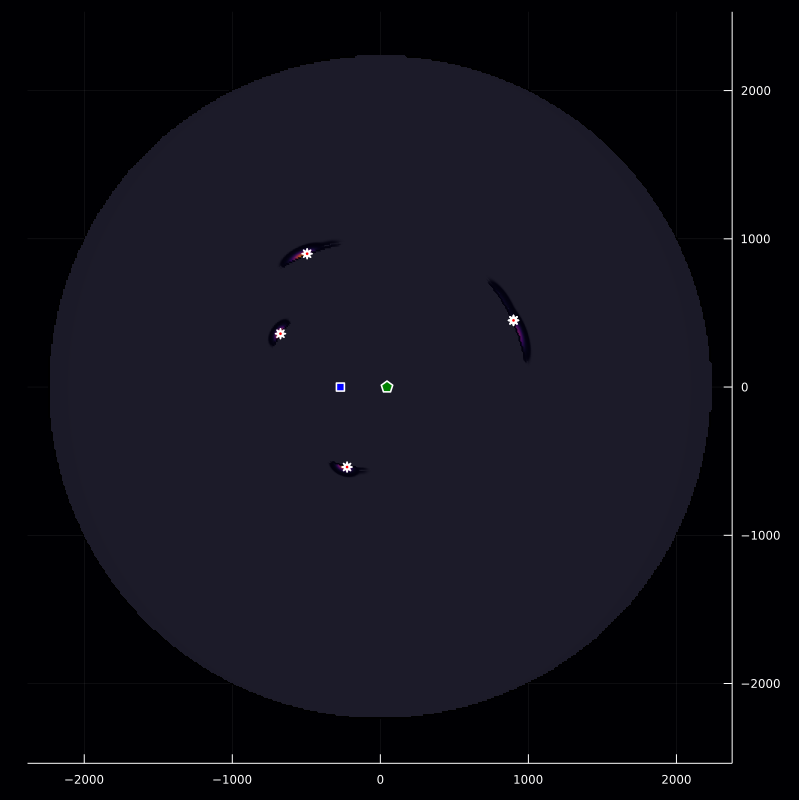
inversePlot2D([q],r,[z],g)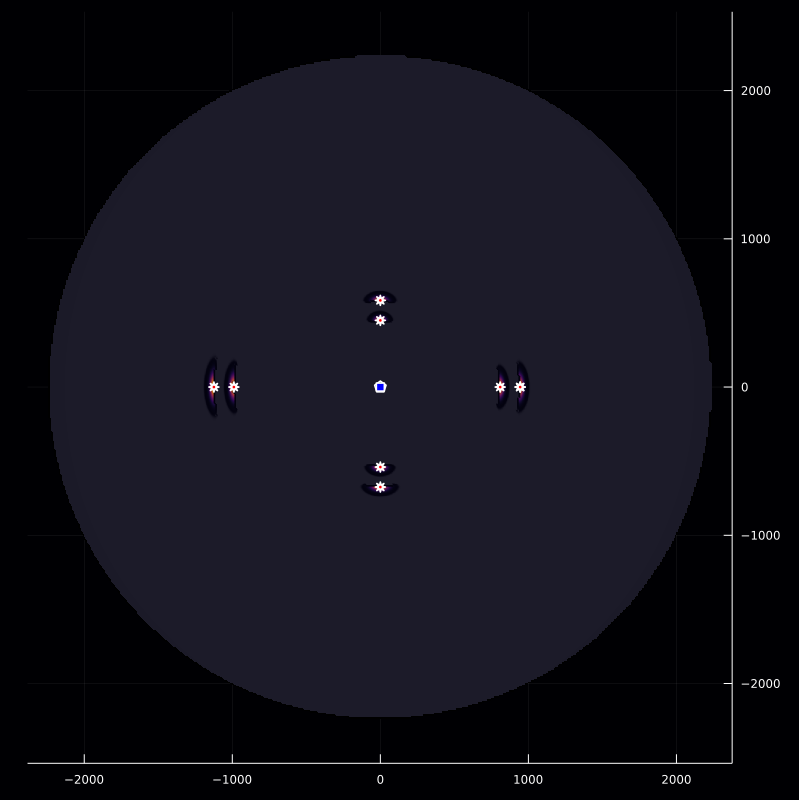
Scenario B (More General Case) [Pulse train, multiple reflector, transmitter and receiver at same location]
Scenario Assumptions
- single stationary directional source with time-varying (rotating) beam center
- single stationary receiver at same location as the source
- multiple stationary ideal point reflectors
- the source emits a periodic impulse train
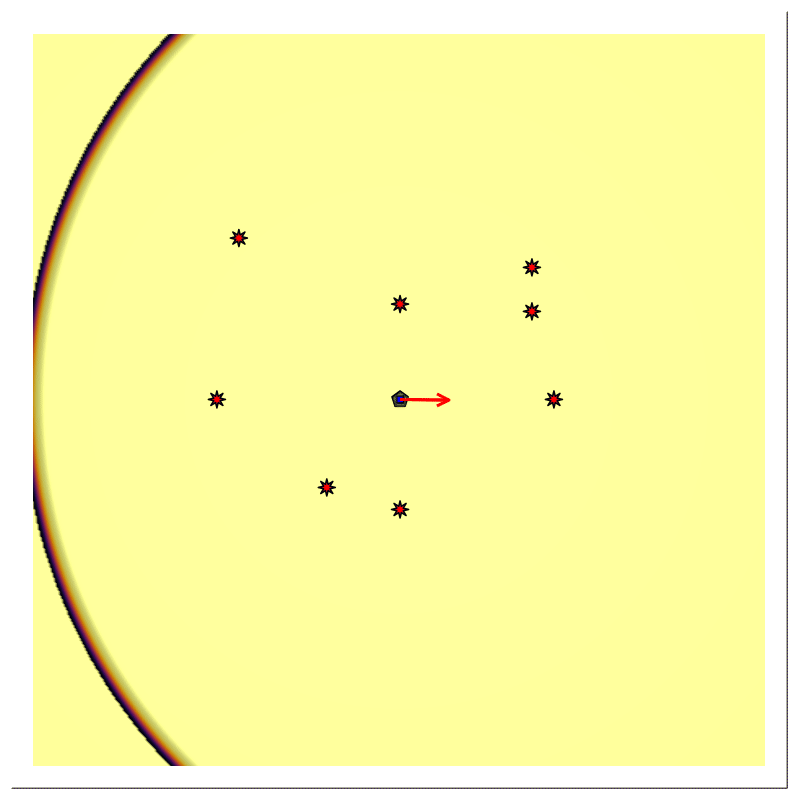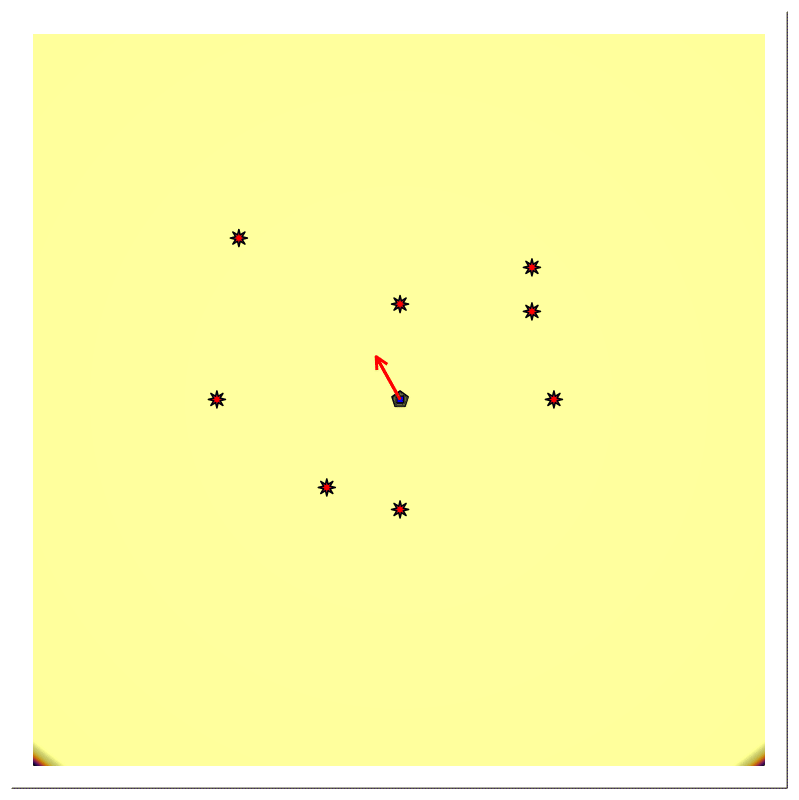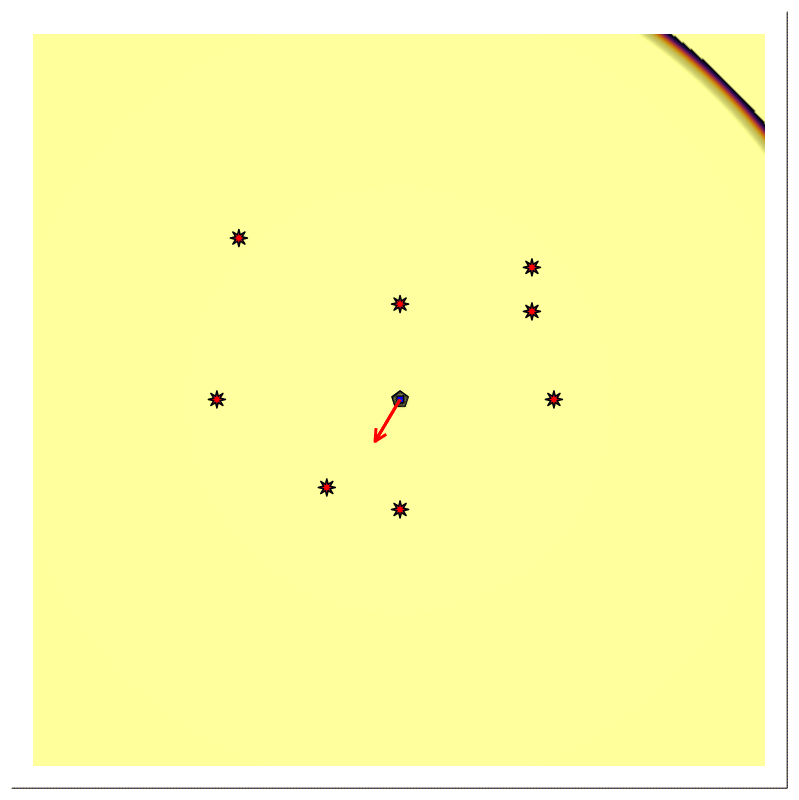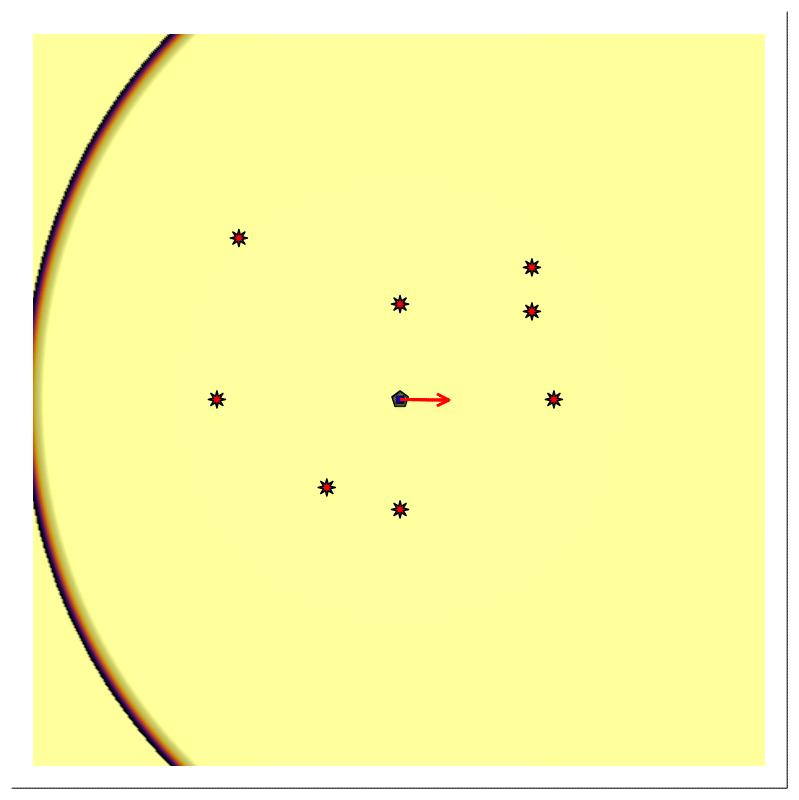
Forward Modeling
For scenario B, we provided the position of the stationary directional source $𝐩ₛ$, with time-varying (rotating) beam center $𝐛(t)$, the stationary receiver's position $𝐩ᵣ$ being at the same location $(𝐩ₛ=𝐩ᵣ)$, the transmitted signal $\mathsf{p}(t)$, and multiple reflector say, N.
Now the expression for the reflector function is given by
\[\mathsf{f}(\bm{\xi}) = \sum\limits_{n=1}^{N}\mathsf{\alpha}_n \delta(\bm{\xi} - \bm{\xi}_n).\]
We compute the reflection due to the directional source as follows
\[\mathsf{r}(\bm{\xi},t) = \sum\limits_{n=1}^{N}\mathsf{\alpha}_n \delta(\bm{\xi} - \bm{\xi}_n) \mathrm{D}_\mathrm{s}\big(\bm{\xi};\,{\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s},\mathbf{b}_\mathrm{s}(\cdot)}\big) \mathsf{A}\left(\frac{\|\bm{\xi}-\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}\|} {\mathrm{c}}\right) \mathsf{p}\left(t-\frac{\|\bm{\xi}-\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}\|}{\mathrm{c}}\right).\]
Finally, the closed form expression of the observed signal, $\mathsf{z}(t)$ is given by
\[\mathsf{z}(t) = \sum\limits_{n=1}^{N} \mathsf{\alpha}_n \mathrm{D}_\mathrm{s}\big(\bm{\xi}_n;\,{\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}, \mathbf{b}_\mathrm{s}(\cdot)}\big)\mathsf{A}^2 \left(\frac{\|\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}-\bm{\xi}_n\|} {\mathrm{c}}\right)\mathsf{p}\left(t -2\frac{\|\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}-\bm{\xi}_n\|}{\mathrm{c}}\right).\]
using LTVsystems
using Plots
𝐩ₛ = [0.0, 0.0]
𝐩ᵣ = [0.0, 0.0]
tₚ = 1.0e-06
T = 15.0e-6
M = 30
p(t) = δn(mod(t-tₚ,T),1.0e-07)
α₁ = -0.7; 𝛏₁ = [0.21c*T,0.0]
α₂ = -0.7; 𝛏₂ = [0.18c*T,0.12c*T]
α₃ = -0.7; 𝛏₃ = [-0.22c*T,0.22c*T]
α₄ = -0.7; 𝛏₄ = [0.0,-0.15c*T]
α₅ = -0.7; 𝛏₅ = [0.18c*T,0.18c*T]
α₆ = -0.7; 𝛏₆ = [0.0,0.13c*T]
α₇ = -0.7; 𝛏₇ = [-0.10c*T,-0.12c*T]
α₈ = -0.7; 𝛏₈ = [-0.25c*T,0.0]
f₀ = 1/(M*T)
𝐛(t) = [cos(2π*f₀*(t-tₚ)),sin(2π*f₀*(t-tₚ))]
G(θ) = 𝒩ᵤ(θ, μ=0.0, σ=π/64)
q = STATsourceD(𝐩ₛ,p,𝐛,G)
r = pointReflector([𝛏₁,𝛏₂,𝛏₃,𝛏₄,𝛏₅,𝛏₆,𝛏₇,𝛏₈],[α₁,α₂,α₃,α₄,α₅,α₆,α₇,α₈],[q])
z = LTIreceiverO(r,𝐩ᵣ)
t=0.0:T/500:M*T
p1 = plot(t,p, xlab="time (sec)", ylab="p(t)", legend=:false)
p2 = plot( t, z(t),ylims=(minimum(z(t)),maximum(z(t))), xlab="time (sec)", ylab="z(t)", legend=:false)
plot(p1,p2,layout=(2,1),size=(800,800))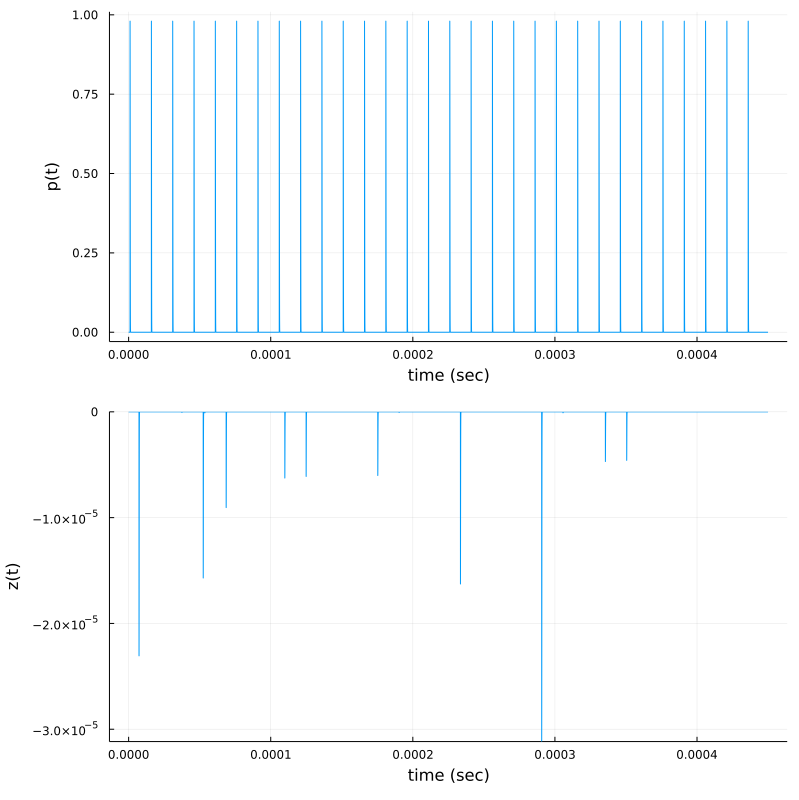
Inverse Modeling
Given the scenario B assumptions, we obtained the received signal, $\mathsf{z}(t)$. Now by considering the transmitted signal as a pulse train given by
\[\mathsf{p}(t)=δ(\mathrm{mod}(t-t_\mathrm{p},\mathrm{T})),\]
we compute the reflector function as follows
\[\hat{\mathsf{f}}(\bm{\xi}) = ∑_{k=1}^{M} \mathsf{f}_k(\bm{\xi}),\]
where $M$ is the number of pulses and $\mathsf{f}_k$ is the reflector function with respect to each periodic pulse given by
\[\mathsf{f}_k(\bm{\xi})=\dfrac{\mathsf{z}\left(t_\mathrm{p}+(k-1)\mathrm{T}+\frac{2\|\bm{\xi}-\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}\|}{\mathrm{c}}\right)\mathrm{D}_{\mathrm{s}k}(\bm{\xi})}{\mathsf{A}^2\big(\frac{\|\bm{\xi}-\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}\|}{\mathrm{c}}\big)},\]
where $\mathrm{D}_{\mathrm{s}k}(\bm{\xi}) = \mathbf{G}\big(∠(𝐛(t_\mathrm{p}+(k-1)\mathrm{T}), \bm{\xi}.-\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s})\big).$
using LTVsystems
using Plots
𝐩ₛ = [0.0, 0.0]
𝐩ᵣ = [0.0, 0.0]
tₚ = 1.0e-06
T = 15.0e-6
M = 30
p(t) = δn(mod(t-tₚ,T),1.0e-07)
α₁ = -0.7; 𝛏₁ = [0.21c*T,0.0]
α₂ = -0.7; 𝛏₂ = [0.18c*T,0.12c*T]
α₃ = -0.7; 𝛏₃ = [-0.22c*T,0.22c*T]
α₄ = -0.7; 𝛏₄ = [0.0,-0.15c*T]
α₅ = -0.7; 𝛏₅ = [0.18c*T,0.18c*T]
α₆ = -0.7; 𝛏₆ = [0.0,0.13c*T]
α₇ = -0.7; 𝛏₇ = [-0.10c*T,-0.12c*T]
α₈ = -0.7; 𝛏₈ = [-0.25c*T,0.0]
f₀ = 1/(M*T)
𝐛(t) = [cos(2π*f₀*(t-tₚ)),sin(2π*f₀*(t-tₚ))]
G(θ) = 𝒩ᵤ(θ, μ=0.0, σ=π/64)
q = STATsourceD(𝐩ₛ,p,𝐛,G)
r = pointReflector([𝛏₁,𝛏₂,𝛏₃,𝛏₄,𝛏₅,𝛏₆,𝛏₇,𝛏₈],[α₁,α₂,α₃,α₄,α₅,α₆,α₇,α₈],[q])
z = LTIreceiverO(r,𝐩ᵣ)
Dₛₖ(ξ::Vector{Float64},k::Int64) = G(angleBetween(𝐛(tₚ+(k-1)*T), ξ.-𝐩ₛ))
fₖ(ξ::Vector{Float64},k::Int64) = ifelse(norm(ξ)>c*T/2, NaN, (z(tₚ+(k-1)*T+(2norm(ξ-𝐩ₛ))./c).*Dₛₖ(ξ,k)./(A(norm(ξ-𝐩ₛ)/c))^2))
g(ξ::Vector{Float64}) = sum(fₖ(ξ,k) for k ∈ 1:M)
inversePlot2D([q],r,[z],g)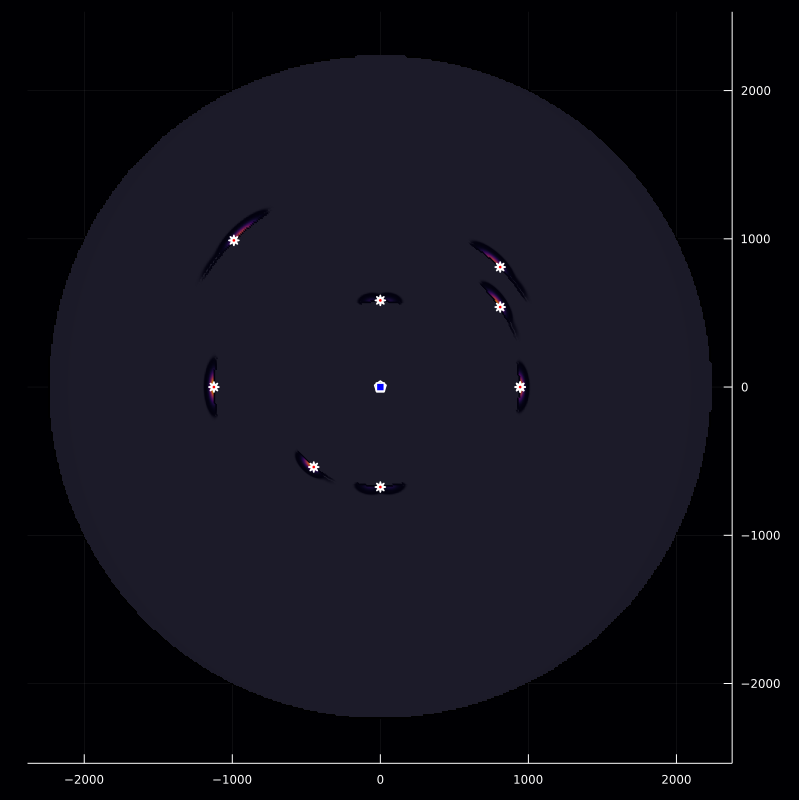
Scenario C [Pulse train, multiple reflector, transmitter and receiver at different location]
Scenario Assumptions
- single stationary source
- single stationary directional receiver with time-varying (rotating) beam center
- multiple stationary ideal point reflector
- the source emits a periodic pulse train
Forward Modeling
For scenario C, we provided the position of the stationary source $𝐩ₛ$, the stationary directional receiver's position $𝐩ᵣ$ with time-varying (rotating) beam center $𝐛(t)$, the transmitted signal $\mathsf{p}(t)$, and multiple reflector say, N.
Now the expression for the reflector function is given by
\[\mathsf{f}(\bm{\xi}) = \sum\limits_{n=1}^{N}\mathsf{\alpha}_n \delta(\bm{\xi} - \bm{\xi}_n).\]
We compute the reflection due to the directional source as follows
\[\mathsf{r}(\bm{\xi},t) = \sum\limits_{n=1}^{N}\mathsf{\alpha}_n \delta(\bm{\xi} - \bm{\xi}_n)\mathsf{A}\left(\frac{\|\bm{\xi}-\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}\|} {\mathrm{c}}\right) \mathsf{p}\left(t-\frac{\|\bm{\xi}-\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}\|}{\mathrm{c}}\right).\]
Finally, the closed form expression of the observed signal, $\mathsf{z}(t)$ is given by
\[\mathsf{z}(t) = \sum\limits_{n=1}^{N} \mathsf{\alpha}_n \mathrm{D}_\mathrm{r}\big(\bm{\xi}_n;\,{\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{r}, \mathbf{b}_\mathrm{r}(\cdot)}\big)\mathsf{A}\left(\frac{\|\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{r}-\bm{\xi}_0\|}{\mathrm{c}}\right) \mathsf{A}\left(\frac{\|\bm{\xi}_0- \mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}\|}{\mathrm{c}}\right)\mathsf{p}\left(t- \frac{\|\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{r}-\bm{\xi}_0\|+\|\bm{\xi}_0- \mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}\|}{\mathrm{c}}\right).\]
using LTVsystems
using Plots
T = 15.0e-6
𝐩ₛ = [0.01c*T, 0.0]
𝐩ᵣ = [-0.06c*T, 0.0]
tₚ = 1.0e-06
M = 32
p(t) = δn(mod(t-tₚ,T),1.0e-07)
α₁ = -0.7; 𝛏₁ = [0.2c*T,0.10c*T]
α₂ = -0.7; 𝛏₂ = [-0.15c*T,0.08c*T]
α₃ = -0.7; 𝛏₃ = [-0.11c*T,0.2c*T]
α₄ = -0.7; 𝛏₄ = [-0.05c*T,-0.12c*T]
f₀ = 1/(M*T)
𝐛(t) = [cos(2π*f₀*(t-tₚ)),sin(2π*f₀*(t-tₚ))]
G(θ) = 𝒩ᵤ(θ, μ=0.0, σ=π/2M)
q = LTIsourceO(𝐩ₛ,p)
r = pointReflector([𝛏₁,𝛏₂,𝛏₃,𝛏₄],[α₁,α₂,α₃,α₄],[q])
z = STATreceiverD(r,𝐩ᵣ,𝐛,G)
t=0.0:T/500:M*T
p1 = plot(t,p, xlab="time (sec)", ylab="p(t)", legend=:false)
p2 = plot( t, z(t),ylims=(minimum(z(t)),maximum(z(t))), xlab="time (sec)", ylab="z(t)", legend=:false)
plot(p1,p2,layout=(2,1),size=(800,800))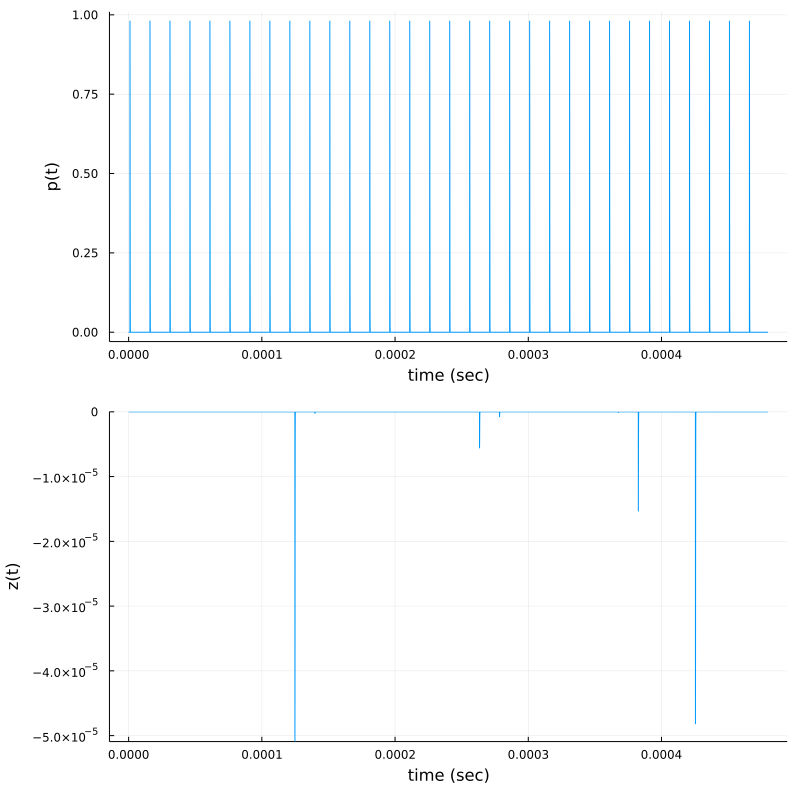
Inverse Modeling
Given the scenario C assumptions, we obtained the received signal, $\mathsf{z}(t)$. Now by considering the transmitted signal as a pulse train given by
\[\mathsf{p}(t)=δ(\mathrm{mod}(t-t_\mathrm{p},\mathrm{T})),\]
we compute the reflector function as follows
\[\hat{\mathsf{f}}(\bm{\xi}) = ∑_{k=1}^{M} \mathsf{f}_k(\bm{\xi}),\]
where $M$ is the number of pulses and $\mathsf{f}_k$ is the reflector function with respect to each periodic pulse given by
\[\mathsf{f}_k(\bm{\xi})=\dfrac{\mathsf{z}\left(t_\mathrm{p}+(k-1)\mathrm{T}+\frac{\|\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{r}-\bm{\xi}\|+\|\bm{\xi}-\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}\|} {\mathrm{c}}\right)\mathrm{D}_{\mathrm{r}k}(\bm{\xi})}{\mathsf{A}\big(\frac{\|\bm{\xi}-\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}\|}{\mathrm{c}}\big) \mathsf{A}\big(\frac{\|\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{r}-\bm{\xi}\|}{\mathrm{c}}\big)},\]
where $\mathrm{D}_{\mathrm{r}k}(\bm{\xi}) = \mathbf{G}\big(∠(𝐛(t_\mathrm{p}+(k-1)\mathrm{T}+\frac{\|\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{r}-\bm{\xi}\|+\|\bm{\xi}-\mathbf{p}_\mathrm{s}\|}{\mathrm{c}}), \mathbf{p}_\mathrm{r}.-\bm{\xi})\big).$
using LTVsystems
using Plots
T = 15.0e-6
𝐩ₛ = [0.01c*T, 0.0]
𝐩ᵣ = [-0.06c*T, 0.0]
tₚ = 1.0e-06
M = 32
p(t) = δn(mod(t-tₚ,T),1.0e-07)
α₁ = -0.7; 𝛏₁ = [0.2c*T,0.10c*T]
α₂ = -0.7; 𝛏₂ = [-0.15c*T,0.08c*T]
α₃ = -0.7; 𝛏₃ = [-0.11c*T,0.2c*T]
α₄ = -0.7; 𝛏₄ = [-0.05c*T,-0.12c*T]
f₀ = 1/(M*T)
𝐛(t) = [cos(2π*f₀*(t-tₚ)),sin(2π*f₀*(t-tₚ))]
G(θ) = 𝒩ᵤ(θ, μ=0.0, σ=π/2M)
q = LTIsourceO(𝐩ₛ,p)
r = pointReflector([𝛏₁,𝛏₂,𝛏₃,𝛏₄],[α₁,α₂,α₃,α₄],[q])
z = STATreceiverD(r,𝐩ᵣ,𝐛,G)
Dᵣₖ(ξ::Vector{Float64},k::Int64) = G(angleBetween(𝐛(tₚ+(k-1)*T.+(norm(ξ-𝐩ₛ).+ norm(𝐩ᵣ.-ξ))./c), 𝐩ᵣ.-ξ))
fₖ(ξ::Vector{Float64},k::Int64) = ifelse(norm(ξ)>c*T/2, NaN, (z(tₚ+(k-1)*T.+(norm(ξ-𝐩ₛ) .+ norm(𝐩ᵣ-ξ))./c).*Dᵣₖ(ξ,k))/(A(norm(ξ-𝐩ₛ)/c).*A(norm(𝐩ᵣ-ξ)/c)))
g(ξ::Vector{Float64}) = sum(fₖ(ξ,k) for k ∈ 1:M)
inversePlot2D([q],r,[z],g)